In an interconnected world where consumer preferences evolve rapidly, the dynamics of the global agricultural sector have become more complex than ever. Rising populations and shifting dietary patterns in developing regions underscore the pivotal role of emerging economies in shaping future demand. This article explores key drivers, market shifts, and the intersection of innovation and sustainability that will determine how agriculture adapts to unprecedented challenges and opportunities.
Global Demand and Shifting Consumption Patterns
Population growth, urbanization, and rising incomes are transforming how food is produced, distributed, and consumed. By 2050, the world’s population is expected to exceed 9 billion, placing enormous pressure on agricultural systems.
Population and Income Effects
- Rapid urbanization leads to shifts from staple grains to higher-value proteins and processed goods.
- Rising middle classes in Asia, Africa, and Latin America demand diverse diets rich in dairy, meat, and fresh produce.
- Income growth fuels consumption of imported goods, creating new opportunities for exporters but also intensifying competition.
As consumer preferences evolve, global supply chains must adapt to ensure food safety, quality, and efficient distribution. The challenge lies in balancing volume with productivity improvements to meet rising food requirements.
Role of Emerging Markets in Driving Growth
Emerging economies are no longer mere buyers of agricultural commodities; they are becoming key influencers in global agri markets.
Regional Case Studies
- China: A leader in rice, wheat, and maize imports, with a strong focus on mechanization and biotechnology to boost yields.
- India: Shifting from subsistence farming to commercial agriculture, leveraging digital platforms to connect farmers with markets.
- Brazil: Major exporter of soybeans and beef, pioneering sustainable practices in the Amazon region.
- Sub-Saharan Africa: High potential for yield gains through targeted investments in irrigation and improved seed varieties.
Investment flows into these markets are rising, from private equity backing agritech startups to government-led infrastructure programs. The integration of globalization with local needs drives policy reforms, fostering an environment where both domestic producers and multinational corporations vie for market share.
Technological Innovation and Sustainable Practices
To cope with climate change, resource constraints, and evolving consumer tastes, the agricultural sector is embracing cutting-edge innovation.
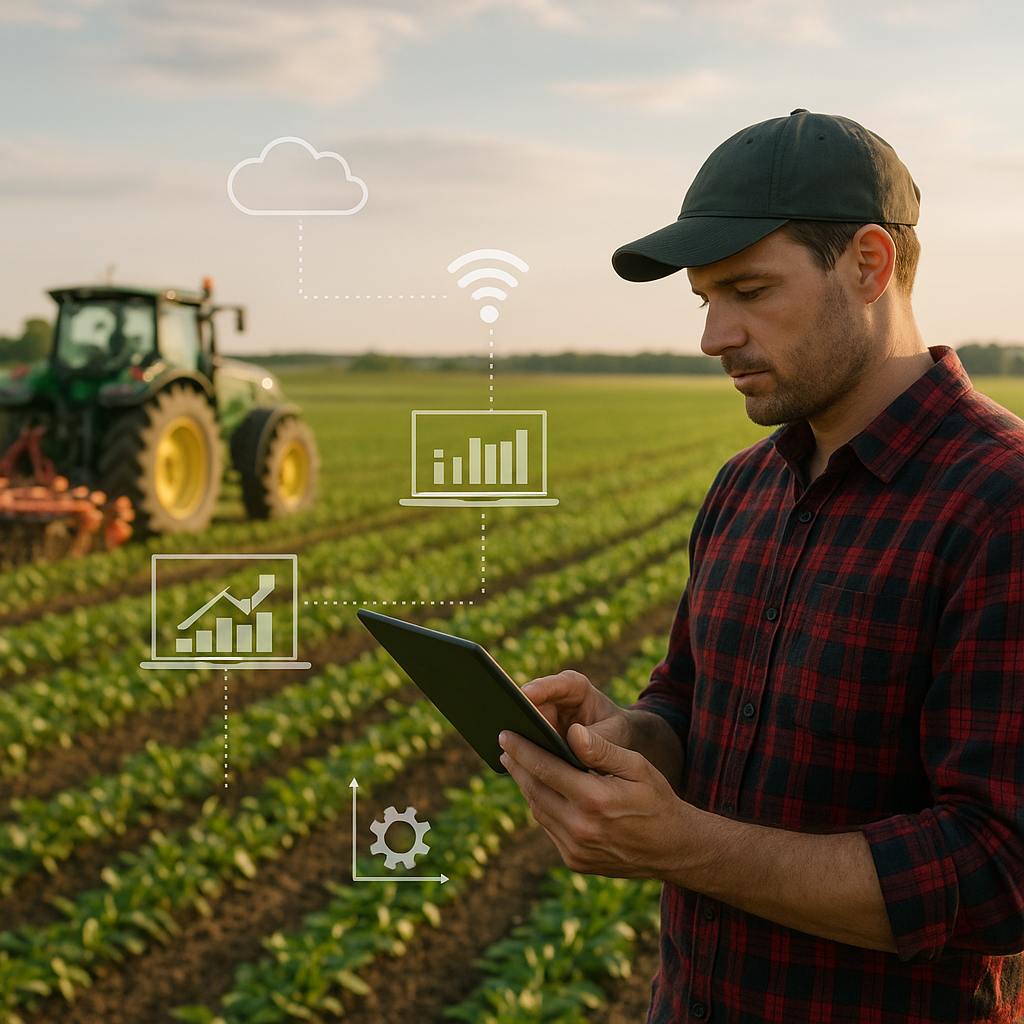
Precision Agriculture and Digital Tools
- Use of drones and satellite imagery for monitoring crop health and optimizing input use.
- IoT-connected sensors that track soil moisture and nutrient levels in real time.
- AI-driven analytics to forecast yields and predict pest or disease outbreaks before they become widespread.
Biotechnology and Crop Improvement
- Gene editing (CRISPR) to develop disease-resistant and climate-resilient varieties.
- Biofertilizers and biopesticides that reduce chemical inputs and improve soil health.
- Vertical farming and hydroponics enabling year-round production in urban settings.
These approaches aim to increase productivity while reducing environmental footprints. Stakeholders are increasingly adopting circular economy concepts, recycling agricultural waste into bioenergy or animal feed, thereby closing resource loops.
Challenges and Future Opportunities
Despite positive trends, the global agri-food system faces significant headwinds. Addressing them will be crucial to unlocking the sector’s full potential.
Key Challenges
- Climate volatility: Droughts, floods, and extreme weather hamper consistent production.
- Resource scarcity: Competition for water and arable land intensifies as urban areas expand.
- Infrastructure gaps: Inadequate storage, transport, and cold-chain networks lead to high post-harvest losses.
- Policy and trade barriers: Tariffs and non-tariff measures can distort markets and hinder efficient allocation of resources.
Emerging Opportunities
- Public-private partnerships for building resilient supply chains and rural infrastructure.
- Impact investing targeting smallholder productivity and climate-smart agriculture.
- Blockchain for transparent traceability, ensuring food safety and fair trade practices.
- Collaborative research initiatives to share knowledge across borders and accelerate sustainability goals.
By fostering innovation ecosystems that integrate farmers, tech providers, policymakers, and financiers, the industry can address challenges and harness opportunities at scale. As agriculture continues its transformation, the synergy between technological breakthroughs and market-driven strategies will shape a resilient, efficient, and equitable global food system.